This section contains information on running the system.
The following commands should be run in separate terminals. Please note, that the system should be installed or built from sources. In each terminal, workspace environment variables should be loaded with command:
source <path_to_ws_velma_os>/devel/setup.bash
(when built from sources) or
source /opt/ws_velma_os/setup.bash
(when installed from a package).
Run roscore:
roscore
Run the control system together with Gazebo simulator:
roslaunch velma_common velma_system.launch
Please wait a few seconds, untill the system is fully loaded - the console will print: “[unpause_on_init-5] process has finished cleanly”. You can ignore error “[ ERROR ][CollisionDetectorComponent::updateHook] no data on port q_INPORT”.
Run the Gazebo Client app that visualizes state of the simulator:
roslaunch rcprg_gazebo_utils gazebo_client.launch
Run the control panel for WUT Velma:
rosrun rqt_velma velma_control_panel.py
and a window will appear:
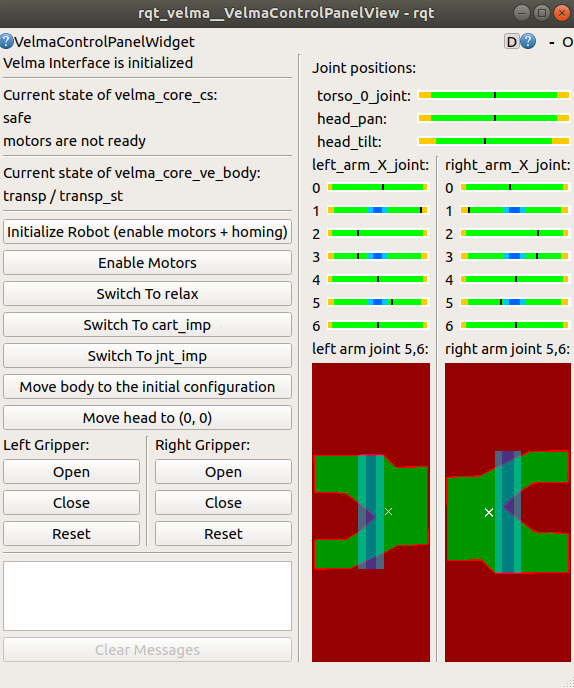
At the initial state, the robot is in “safe” state, and “motors are not ready” for operation. Hit the “Initialize robot” button to enable motors and to perform homing procedure. After the homing is done, click “Move body to the initial configuration”. Now, the state should be “jnt_imp”, i.e. the robot in is joint impedance mode.
Run ROS rviz to visualize the kinematic state of the robot:
rosrun rviz rviz
In rviz, add “RobotModel” and change “Global Options” -> “Fixed frame” to “world”.
Please refer to the next sections for more detailed description of the presented commands and for information on other features and tools.