Introduction
The main goal of this task is to learn to control a robot using multiple behaviours governed by a finite state machine (FSM).
Finite State Machines are a useful tool for programming robots. There are many resources you can read to undestand the concept of FSM, e.g. this article
Your task is to generate a trajectory that uses both trajectory generators from the Task 1 and Task 2. The robot should follow a rounded rectangle path that consists of two half circles and two straight lines:
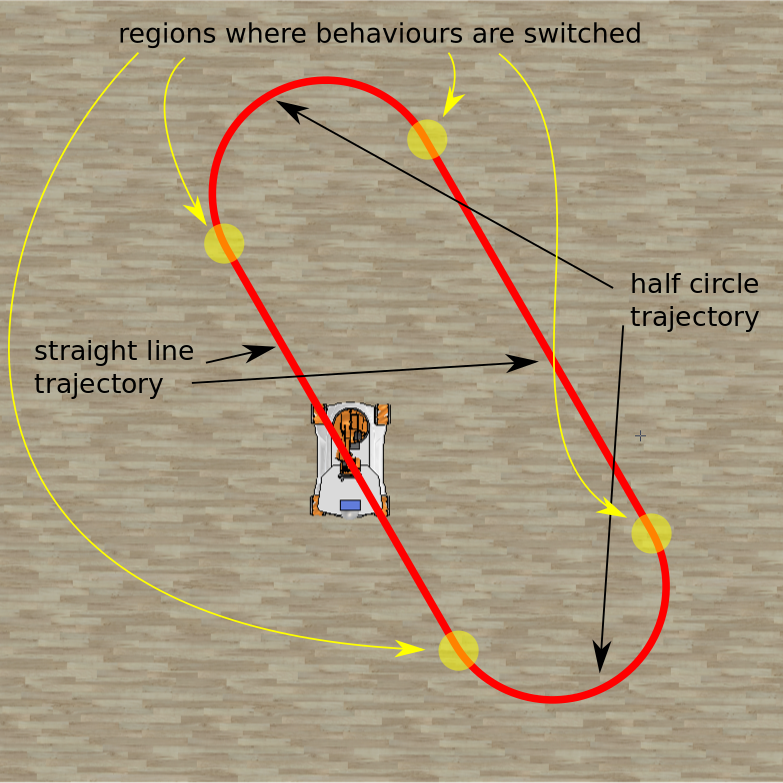
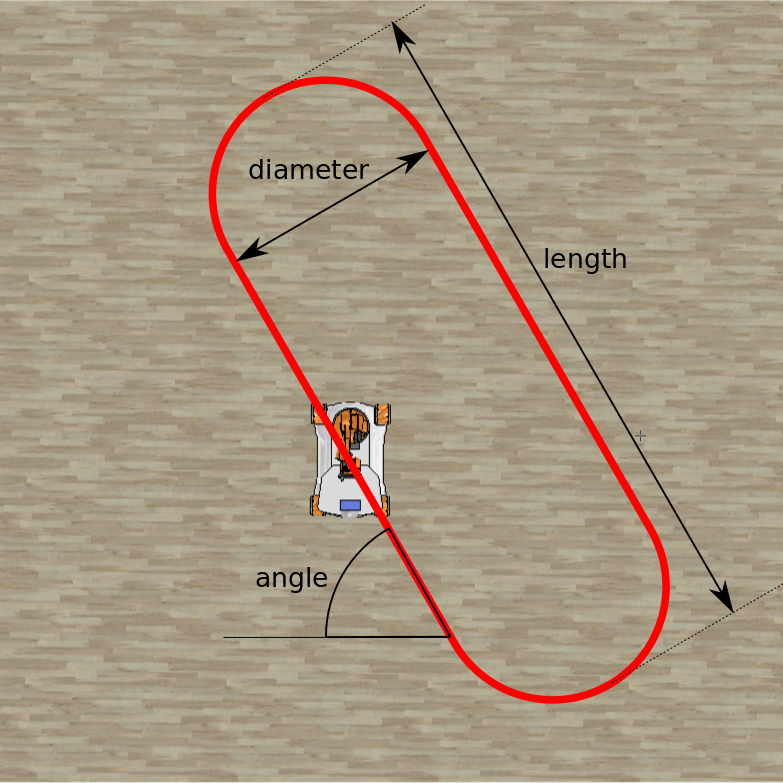
There are three parameters that describe the path: diameter, length and angle:
You should write a script solution3.m that implements a callback function solution3.
The parameters are passed to the control program through the variable-length
argument list in the run_simulation function, e.g. run_simulation(@solution3, false, 1, 3, 0.5)
where the arguments are:
solution3is the name of your control callback functionfalse- do not display the sensor data (simulation runs faster)1- the diameter of the rouded rectangle (this is an example value)3- the length of the rouded rectangle (this is an example value)0.5- the angle of the rouded rectangle (in radians, this is an example value)
The callback function for this task must be declared as:
function [forwBackVel, leftRightVel, rotVel, finish] = solution3(pts, contacts, position, orientation, varargin)
% The control loop callback function - the solution for Task 3
% get the parameters
if length(varargin) ~= 3,
error('Wrong number of additional arguments: %d\n', length(varargin));
end
param_diameter = varargin{1};
param_length = varargin{2};
param_angle = varargin{3};
% declare the persistent variable that keeps the state of the Finite
% State Machine (FSM)
persistent state;
if isempty(state),
% the initial state of the FSM is 'init'
state = 'init';
end
% initialize the robot control variables (returned by this function)
finish = false;
forwBackVel = 0;
leftRightVel = 0;
rotVel = 0;
% TODO: manage the states of FSM
...
end
Please refer to solution solution0a in the Example Task for more details on variable-length argument list.
Task requirements
- The name of the control callback function should be
solution3 - Both position and orientation must be controlled
- The robot must follow the desired path
- The robot can move infinitelly
- Use the environment file
~/emor_trs/youbot/vrep_env/exercise01.ttt
Grading
You can get 5 points, including:
- proper implementation of the FSM: states, transitions, conditions, etc.
- proper use of all parameters